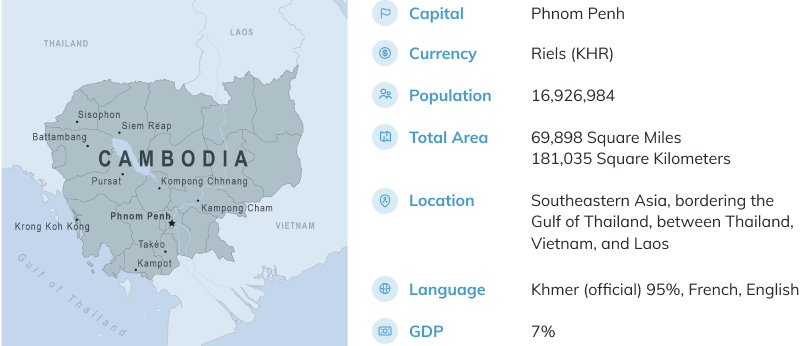
Cambodia
1. Profile
2. Economy & Industry
The economy of Cambodia currently follows an open market system and has seen rapid economic progress in the last decade. Although Cambodia’ GDP is rapidly increasing, is low compared with most neighboring countries.
Cambodia's two largest industries are textiles and tourism, while agricultural activities remain the main source of income for many Cambodians living in rural areas. The tourism, garment, construction and real estate, and agriculture sectors accounted for the bulk of growth. Mining also is attracting some investor interest and the government has touted opportunities for mining bauxite, gold, iron and gems.
Currently, Cambodia's foreign policy focuses on establishing borders with neighbors (such as Thailand and Vietnam), as well as integrating itself into ASEAN & WTO. Cambodia continues to attract investors because of its low wages, plentiful labor and favorable tax treatment.
- Major Industries: tourism, garments, construction, rice milling, fishing, wood and wood products, rubber, cement, gem mining, textiles.
- Agriculture Products: rice, rubber, corn, vegetables, cashews, cassava (manioc, tapioca), silk.
_IMNm76X33.png)
3. FDI Attraction
FDI inflows to Cambodia have grown exponentially in the last few years due to sound macroeconomic policies, political stability & high economic growth. According to 2020 World Investment Report by UNCTAD, Cambodia recorded its highest ever FDI in 2019, mainly due to robust investments in manufacturing and services.
The main investing countries are China, Japan, Hong Kong, the US and the Netherlands and others ASEAN countries. The construction industry attracts the largest share of foreign investors, followed by infrastructure, industry (primarily textiles), agriculture and tourism.
Source: UNCTAD's World Investment Report
4. Export & Import:
- Major Exports: computers, office machine parts, transistors, rubber, vehicles (cars and trucks), plastic, seafood.
- Top Export Partners: US, Japan, Singapore, Hong Kong, China
- Major Imports: capital goods, intermediate goods and raw materials, consumer goods, fuels.
- Top Import Partners: Japan, US, China, Malaysia, Singapore Source: www.countryreports.org
5. Infrastructure in Cambodia
Road Transport
Roads are the dominant mode of transportation in Cambodia, accounting for 65% of freight movement and 87% of passenger’s traffic. About 50% of the roads and highways are hard surfaced, all-weather, and in good condition.
Cambodia considers to develop two expressways in order to serve the growing extent of economy and trade. The first line will lead from the capital Phnom Penh to the coastal Preah Sihanouk province with a total length of 230 km. The second one will lead from Phnom Penh to Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam with a total length of 213 km. Funded by over $3 billion of Chinese loans, Chinese companies have built 3,000 km of roads as well as several major bridges.
Railway
Cambodia has 612km of 1000mm metre gauge rail network and two rail lines, both originating in Phnom Penh of, in total around 600 kilometers of single, one-meter-gauge track. The first line was built in 1942 and runs from Phnom Penh to Poipet at the Thai border. The second line, running from Phnom Penh to Sihanoukville at the southern finished at 1969. China Railway Group is planning to build a 405 km north-south railway across Cambodia, which would support the planned expansion of the steel industry in Cambodia.
_jedoYe2Pp.png)
Waterways Transport
The three main international ports in Cambodia are: Sihanoukville on the Gulf of Siam, Phnom Penh on the Mekong river and Koh Kong provincial port
Sihanoukville Port:
Sihanoukville is the main deep-sea port of Cambodia. The Port of Sihanoukville, situated in the Bay of Kompong Som, is the principal and only deep-water maritime port of Cambodia. In 1993, 15,000 TEU's passed through Sihanoukville Port. 80% of the containers had origin/destination in Singapore.
_A5WfeRFG9.png)
Phnom Penh Port:
The Phnom Penh port is the country's traditional river port, accessible to vessels from the South China Sea through Vietnam. Phnom Penh port is located in-the city, around 330 km from the mouth of the Mekong of which about 100 km is in Cambodia. The port serves up to 150 ships/year.
Koh Kong Port:
Koh Kong is situated near the Thai border and is used by small boats, below 500 dwt, is also a quite an important fishing port. Up to 300-tonne capacity boats can be accepted, or 500 tonnes at anchorage.
Air Transport:
The country possesses 26 airfields, of which 8 airfields had permanent-surface runways. Phnom Penh International Airport in Phnom Penh is the largest airport; it also serves as the main base for the renascent Cambodian Air Force. Angkor International Airport is second largest airport in the city of Siem Reap. Cambodia Angkor Air is the largest airline in the country, owned by the Cambodian government (51%) and Vietnam Airlines (49%).






